The preview of Kafka Streams, which is one of the main features of the upcoming Apache Kafka 0.10, was announced by Jay Kreps this week.
Kafka joins the Stream Processing club
Kafka Streams is a library to build streaming applications using Kafka topics as input/output. Kafka Streams is in the same league as other streaming systems such as: Apache Storm, Apache Flink and, not surprisingly, Apache Samza which also uses Kafka for input or output of streams.
One of the main advantages is that if you’re already using Apache Kafka and you need real-time processing, you just need to use the library and you are good to go.
Other important features are: stateful processing, windowing and ability to be deployed using your preferred solution: a simple command line, Mesos, YARN or kubernetes and docker if you’re a container party boy.
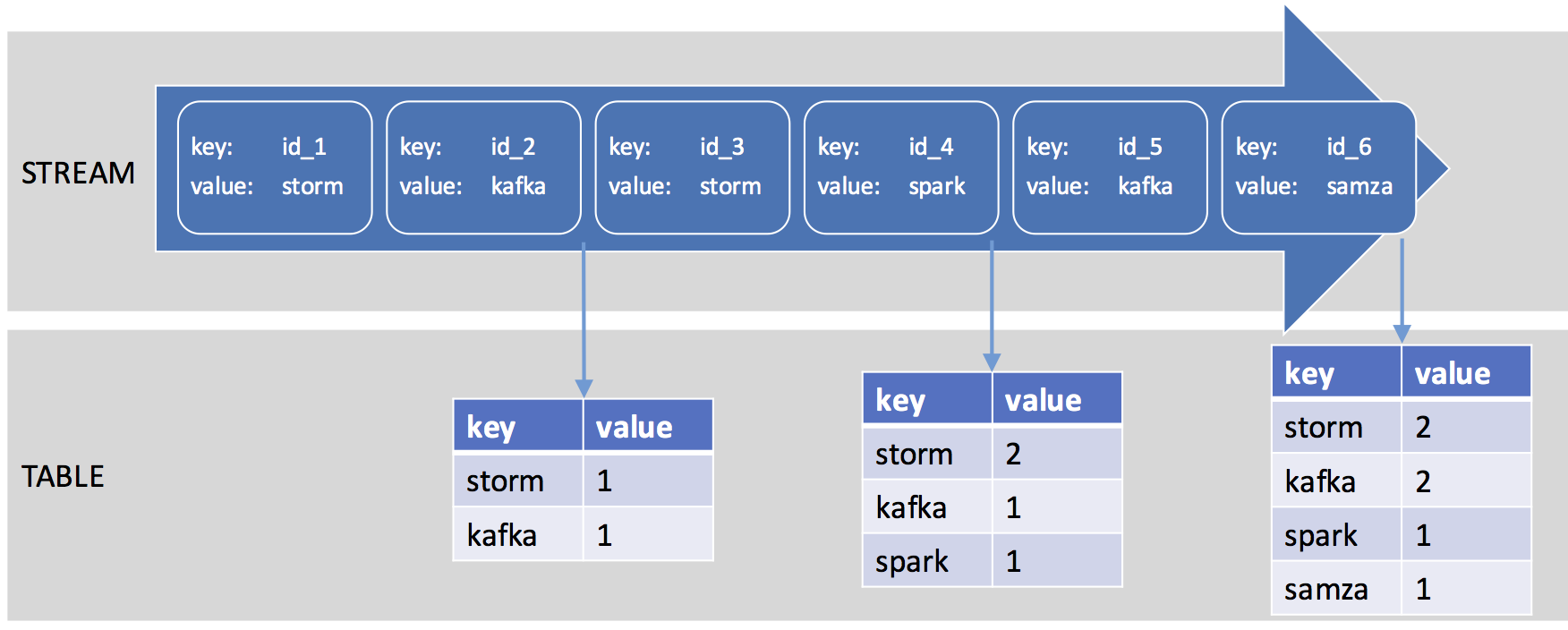
Streams and Tables
One of the key concepts in Kafka Streams is the support of KStream and KTable.
That isn’t a new concept if you come from the Event Sourcing world: the KStream is the append-only event store where its state is given by replaying the events from the beginning of time until the last event whereas KTable is the snapshot or projection of the current state of the stream given a point in time.
Example: Twitter Hashtags Job
Show me the code!
You can find the complete example here: https://github.com/mserrate/kafka-streams-app
1 | KStream<String, JsonNode> source = builder.stream(stringDeserializer, jsonDeserializer, "streams-hashtag-input"); |
For this example I’ve been using a simple TweetProducer who connects to the Twitter Streaming API and sends JSON events to a Kafka topic.
This topic is read as a KStream and then we begin the process:
- Filter out the tweets without hashtags
- Apply a flatMapValues (we are just interested in the values, not the keys) to split the different hashtags in a tweet
- Apply a map to return a key (hashtag) value (hashtag) as we want to aggregate by hashtag
- Aggregate the streams per key (the hashtag) and count them
Finally we send the KTable to the output queue.